Sally Kang
why join the navy.
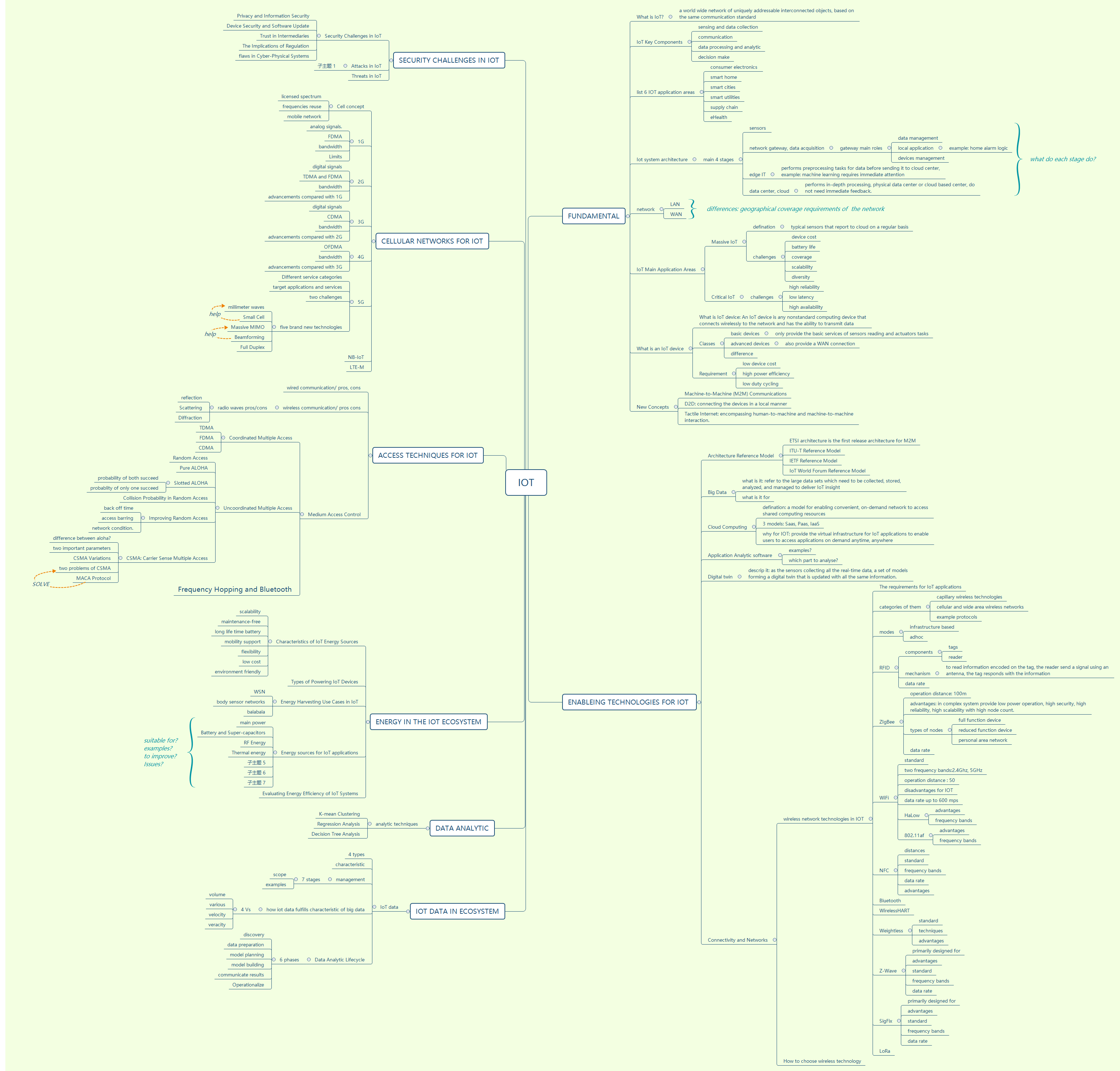
Notes for IoT
[
IoT Critical Infrastructure
Fundamental
What is IoT?
- A world wide network of uniquely addressable interconnected objects, based on the same communication standard
IoT Key Components
- sensing and data collection
- communication
- data processing and analytic
- decision make
list 6 IOT application areas
- consumer electronics
- smart home
- smart cities
- smart utilities
- supply chain
- eHealth
Iot system architecture
main 4 stages
- sensors
- network gateway, data acquisition
- gateway main roles
- data management
- local application example: home alarm logic
- devices management
- edge IT
- performs preprocessing tasks for data before sending it to cloud center, example: machine learning requires immediate attention
- data center, cloud
- performs in-depth processing, physical data center or cloud based center, do not need immediate feedback.
what do each stage do?
(sensors , network gateway, data acquisition, edge IT, data center, cloud)
network
- LAN
- WAN
- differences: geographical coverage requirements of the network (LAN, WAN)
IoT Main Application Areas
-
Massive IoT
- defination: typical sensors that report to cloud on a regular basis
-
challenges
- device cost
- battery life
- coverage
- scalability
- diversity
Critical IoT
- challenges
- high reliability
- low latency
- high availability
What is an IoT device
-
What is IoT device: An IoT device is any nonstandard computing device that connects wirelessly to the network and has the ability to transmit data
-
Classes
-
basic devices: only provide the basic services of sensors reading and actuators tasks
-
advanced devices: also provide a WAN connection
-
-
difference
- Requirement
- low device cost
- high power efficiency
- low duty cycling
- Requirement
New Concepts
-
Machine-to-Machine (M2M) Communications
-
D2D: connecting the devices in a local manner
-
Tactile Internet: encompassing human-to-machine and machine-to-machine interaction.
Enabling Technology For IOT
Architecture Reference Model
- ETSI architecture is the first release architecture for M2M
- ITU-T Reference Model
- IETF Reference Model
- IoT World Forum Reference Model
Big Data
-
what is it: refer to the large data sets which need to be collected, stored, analyzed, and managed to deliver IoT insight
-
what is it for
Cloud Computing
-
defination: a model for enabling convenient, on-demand network to access shared computing resources
-
3 models: Saas, Paas, IaaS
-
why for IOT: provide the virtual infrastructure for IoT applications to enable users to access applications on demand anytime, anywhere
Application Analytic software
- examples?
- which part to analyse?
- Digital twin
- descrip it: as the sensors collecting all the real-time data, a set of models forming a digital twin that is updated with all the same information.
Connectivity and Networks
- wireless network technologies in IOT
- The requirements for IoT applications
- categories of them
- capillary wireless technologies
- cellular and wide area wireless networks
-
example protocols
-
modes
-
infrastructure based
-
adhoc
- RFID
- components
- tags
- reader
- mechanism : To read information encoded on the tag, the reader send a signal using an antenna, the tag responds with the information
- data rate
- components
-
ZIgBee
-
operation distance: 100m
-
advantages: in complex system provide low power operation, high security, high reliability, high scalability with high node count.
-
types of nodes
-
full function device
-
reduced function device
-
-
-
personal area network
-
data rate
-
WiFi
-
standard
-
two frequency bands:2.4Ghz, 5GHz
-
operation distance : 50
-
disadvantages for IOT
-
data rate up to 600 mps
-
-
HaLow
-
advantages
-
frequency bands
-
802.11af
-
advantages
-
frequency bands
-
-
NFC
- distances
- standard
- frequency bands
- data rate
- advantages
-
Bluetooth
-
WirelessHART
-
Weightless
- standard
- techniques
- advantages
-
Z-Wave
- primarily designed for
- advantages
- standard
- frequency bands
- data rate
- SigFix
- primarily designed for
- advantages
- standard
- frequency bands
- data rate
-
LoRa
- How to choose wireless technology
Iot data in ecosystem
- IoT data
- 4 types
- characteristic
- management
- 7 stages
- scope
- examples
-
how iot data fulfills characteristic of big data
-
4 Vs
- volume
- various
- velocity
- veracity
-
- Data Analytic Lifecycle
-
6 phases
- discovery
- data preparation
- model planning
- model building
- communicate results
- Operationalize
-
-
Data Analytic
-
analytic techniques
- K-mean Clustering
- Regression Analysis
- Decision Tree Analysis
-
Energy in the IoT Ecosystem
Characteristics of IoT Energy Sources
- scalability
- maintenance-free
- long life time battery
- mobility support
- flexibility
- low cost
- environment friendly
Types of Powering IoT Devices
-
Energy Harvesting Use Cases in IoT
-
WSN
-
body sensor networks
-
So on
-
Energy sources for IoT applications
- main power
- Battery and Super-capacitors
- RF Energy
- Thermal energy
- suitable for?
- examples?
- to improve?
- Issues?
Evaluating Energy Efficiency of IoT Systems
-
Access Techniques for IoT
-
wired communication/ pros, cons
-
wireless communication/ pros cons
-
radio waves pros/cons
- reflection
- Scattering
- Diffraction
-
-
Medium Access Control
-
Coordinated Multiple Access
- TDMA
- FDMA
- CDMA
-
Uncoordinated Multiple Access
- Random Access
- Pure ALOHA
- Slotted ALOHA
- probability of both succeed
- probablity of only one succeed
-
-
Collision Probability in Random Access
- Improving Random Access
- back off time
- access barring
- network condition.
-
CSMA: Carrier Sense Multiple Access
- difference between aloha?
- two important parameters
- CSMA Variations
- two problems of CSMA
-
MACA Protocol
- Frequency Hopping and Bluetooth
Cellular Networks for IoT
-
Cell concept
- licensed spectrum
- frequencies reuse
- mobile network
-
1G
- analog signals.
- FDMA
- bandwidth
- Limits
-
2G
- digital signals
- TDMA and FDMA
- bandwidth
- advancements compared with 1G
-
3G
- digital signals
- CDMA
- bandwidth
- advancements compared with 2G
-
4G
- OFDMA
- bandwidth
- advancements compared with 3G
-
5G
- Different service categories
- target applications and services
- two challenges
-
five brand new technologies
- millimeter waves
- Small Cell
- Massive MIMO
- Beamforming
- Full Duplex
- NB-IoT
- LTE-M
Security Challenges in IoT
- Security Challenges in IoT
- Privacy and Information Security
- Device Security and Software Update
- Trust in Intermediaries
- The Implications of Regulation
- flaws in Cyber-Physical Systems
- Attacks in IoT
- Threats in IoT